“Quit worrying about your health. It’ll go away.” - Robert Orben
As people with diabetes (type 1 or 2), we know our bodies are under extra stress. This is due to things like fluctuating blood sugars and chronic inflammation. These factors can gradually accumulate into nerve damage and a variety of other long-term complications.
However, we have recently learned that some “long-term complications” are functional and reversible (at least in their early stages). One way to reverse them is slow breathing.
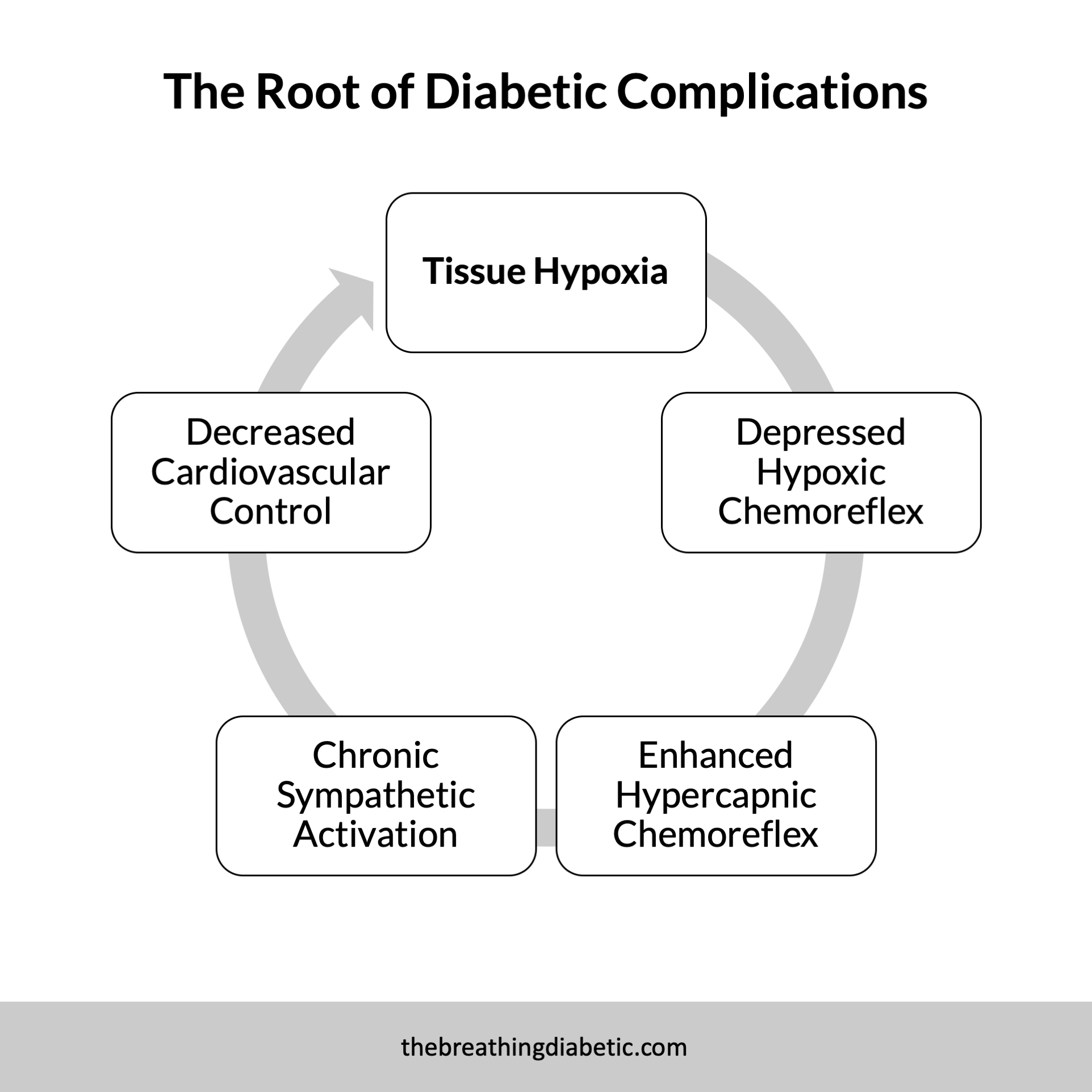
Slow breathing treats the root cause of many complications, tissue hypoxia, which then restores autonomic functioning. This has been proven in several studies involving people with type-1 diabetes. However, most participants had not yet developed severe complications.
Putting Slow Breathing to the Test
It seems reasonable to assume that slow breathing would have the same effects in type 2s. But, what if these people with type-2 diabetes have chronic kidney disease? With a severe complication such as this, could slow breathing still have the same benefits?
Trained breathing-induced oxygenation acutely reverses cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal disease
Published in Acta Diabetologica, 2016
The Study Group and Breathing Protocol
This study had 26 type-2 diabetic patients, 12 of which had diabetic kidney disease, and 24 non-diabetic controls. The protocol was simple: They had the participants lay down and breathe normally for five minutes, followed by two minutes of slow breathing at 6 breaths per minute.
The primary outcome was a change in baroreflex sensitivity (BRS). BRS measures your body’s ability to quickly adjust blood pressure to meet the current demands of your situation. It is thought to be an overall measurement of autonomic and cardiovascular control. In general, diabetics have lower BRS scores than non-diabetics.
Slow Breathing Improves Autonomic Function in Diabetics With Kidney Disease
At baseline, the type-2 diabetics had a lower resting oxygen saturation and lower BRS. When they switched to breathing at 6 breaths per minute, their oxygen saturation and BRS both increased significantly. Their blood pressure also reduced.
Perhaps most importantly, these same changes were observed in the diabetics with kidney disease. Both sets of diabetics (kidney disease and no complications) showed similar increases in BRS and oxygen saturation. This indicates that, even in diabetics with severe complications, slow breathing can acutely reverse autonomic dysfunction.
Getting Back to Tissue Hypoxia
The authors suggest that these improvements in autonomic function were due to increases in tissue oxygenation. Similar to the study we featured on type-1 diabetes, they indicate that by increasing tissue oxygen levels, sympathetic activity is reduced, and autonomic balance is restored.
A New Model of Diabetic Complications
These results again indicate that autonomic dysfunction is not an expression of nerve damage. Instead, it is a reversible phenomenon that might actually be the precursor to nerve damage. This paradigm-shifting view opens the door to new opportunities for treating autonomic dysfunction in diabetics.
In good breath,
Nick
P.P.S. James Nestor’s new book, Breath: The New Science of a Lost Art, comes out tomorrow. I don’t know James, but from the podcast interviews I’ve heard so far, this sounds like a must-read if you’re into all this “breathing” stuff :)
And if you really want to geek out, James and Patrick McKeown got together for an hour long conversation on all things breathing. Watch/Listen Here.