Since we cannot know all that there is to be known about anything, we ought to know a little about everything.” - Blaise Pascal
People with diabetes are at an increased risk of cardiovascular and autonomic problems. Diabetics also display altered respiratory control, for example, showing depressed (or enhanced) chemoreflexes.
However, previous studies have never examined these two aspects in an integrated fashion.
Integration Over Isolation
The problem with separately studying these systems is that the results might not be independent. For example, if a study shows that diabetics have decreased respiratory control, it might conclude that this is from diabetic nerve damage.
Likewise, if a study shows that cardiovascular function is depressed, it might also conclude that this is due to diabetic nerve damage.
However, if we study them together, we might find that there is a reciprocal relationship. Maybe the respiratory problems are causing cardiovascular issues? Perhaps it’s the other way around?
This study takes that approach and has some pretty remarkable conclusions.
Integrated cardiovascular/respiratory control in type 1 diabetes evidences functional imbalance: Possible role of hypoxia
(Click Here to Read Full Summary — I don’t say this often, but please read this one if you have diabetes)
Published in the International Journal of Cardiology, 2017.
In forty-six type-1 diabetics and 103 age-matched controls, they measured baroreflex sensitivity (BRS) as a marker of cardiovascular function and chemoreflexes as a marker of respiratory control.
Chemoreflexes estimate how sensitive you are to increasing CO2 (hypercapnic chemoreflex) and decreasing O2 (hypoxic chemoreflex).
The Hypothesis: If BRS and chemoreflexes are reduced, this would suggest diabetic nerve damage. However, if some are reduced while others are elevated, this reciprocal relationship might be showing autonomic dysfunction instead of diabetic nerve damage.
This is such an important distinction. “Damage” implies that the damage is done. “Dysfunction” implies that we could make it functional again.
Diabetics Have Worsened Cardiovascular and Respiratory Control
The results showed that subjects with diabetes had a lower BRS than the controls. They also had a suppressed hypoxic chemoreflex. However, they had an elevated hypercapnic chemoreflex. (Remember their hypothesis: if it was nerve damage, both of these chemoreflexes would be reduced.)
Interestingly, the diabetics also showed a lower oxygen saturation. And, they also had relatively high HbA1c’s (an average of 8.19%). A high HbA1c will decrease oxygen delivery to the tissues and cells.
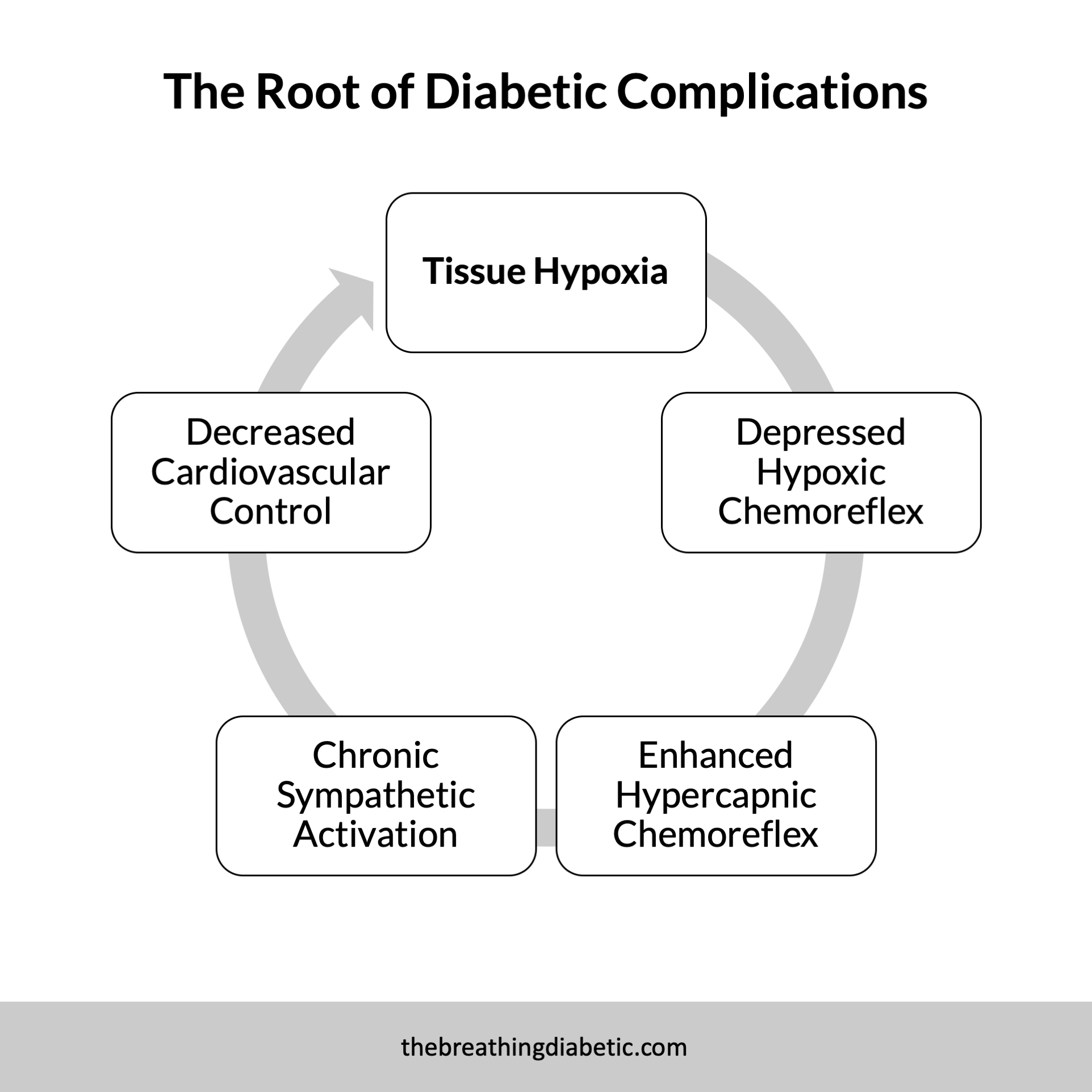
Tissue Hypoxia is at the Root of Diabetic Complications
The reduced oxygen saturation and high HbA1c suggest a resting state of tissue hypoxia in diabetes. Over time, we become “numb” to this, which explains the decreased hypoxic chemoreflex.
The body compensates with an up-regulated hypercapnic chemoreflex, which leads to chronic activation of the sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight). Chronic sympathetic activation then suppresses our cardiovascular control.
It’s a vicious cycle with negative long-term implications:
Dysfunction, not Damage: A Silver Lining
“We show in the present study that what is normally called ‘autonomic neuropathy’ could be in many cases a functional condition of sympathetic activation, driven by many factors, one of which seems to be resting hypoxia.”
This is all actually good news. Their results suggest that diabetic autonomic imbalance is mainly functional and not related to nerve damage. In fact, the authors suggest that this imbalance likely leads to nerve damage, rather than being the result of it. Therefore, therapies targeting cardio-respiratory control could help reverse/prevent diabetic complications if caught early enough.
Break Out Your Slow Breathing Hammer
What are these therapies? One is slow breathing. Slow breathing will immediately improve cardiovascular and respiratory reflexes. It will also enhance oxygenation (when breathing through the nose).
I hate sounding like all I have is a “slow breathing hammer,” but it is just too important not to stress over and over again.
Here’s to taking the first step toward protecting our long-term health as diabetics.
In good breath,
Nick
P.S. A great podcast was recently released with James Nestor, author of the soon-to-be-released book: “Breath - The New Science of a Lost Art”. (The book looks terrific, so I pre-ordered my copy about a week ago.)
You can basically learn everything you’ll ever need to know about breathing in this quick 35-minute interview. I loved it.